In this guide we’ll be covering the process to install PIP on Ubuntu using the command line. By following these simple steps, you can install PIP quickly and easily.
What is PIP?
PIP stands for Pip Installs Packages. It is a package manager for the Python programming language that allows you to download and install Python packages and their dependencies on a Linux system. It is similar to a Linux distribution’s package manager, but it is specifically designed for Python packages. PIP can be installed on any major Linux distribution and is available for both Python 2 and Python 3. Once installed, PIP can be used on the command line to download and install Python packages and their dependencies.
Installing PIP on Ubuntu
To begin, you first need to log in and connect to your server via SSH. See here for common SSH clients:
SSH client utilities (Free):
PuTTY:
https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/latest.html
Bitvise SSH client:
https://www.bitvise.com/ssh-client-download
KiTTY:
https://www.9bis.net/kitty/
MobaXterm (Free with available Paid Pro version):
https://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/
SmarTTY:
https://sysprogs.com/SmarTTY/
Solar-PuTTY (Free with available paid versions):
https://www.solarwinds.com/free-tools/solar-putty
There are many others available out there as well.
1. Log in to your Ubuntu server with root user using your favorite SSH client.
2. Once logged in, Update system packages with the command below.
apt update
![]() Which will start collecting information from all the repositories in your system
Which will start collecting information from all the repositories in your system
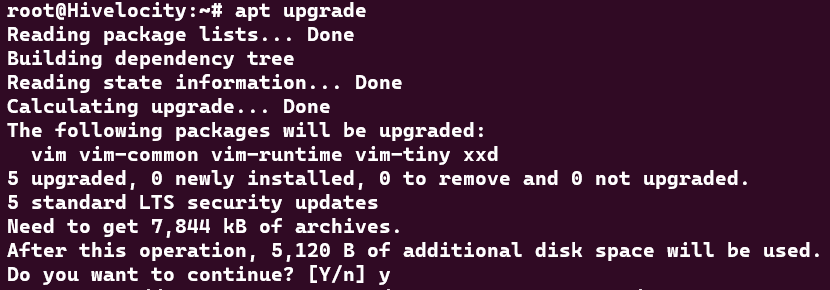
 3. Once the update of repositories is done, proceed to upgrade the packages.
3. Once the update of repositories is done, proceed to upgrade the packages.
apt upgrade
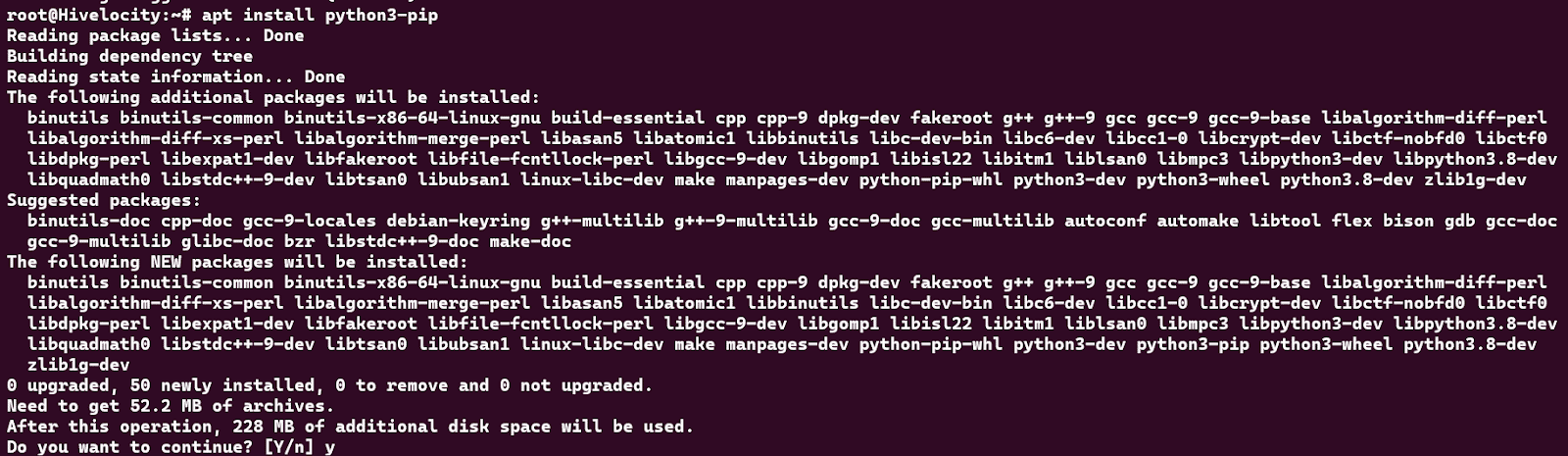
4. The last step is to install python-PIP and any other required packages using the command:
apt install python3-pip
5. Verify the installation has been completed successfully with the command:
pip –V

If all went well and you are seeing the above output, then you should now be ready to use PIP.
And there you have it! Now that you’ve successfully installed PIP on Ubuntu, you’re ready to start using python-based software.
Looking for more information on Ubuntu? Search our Knowledge Base!