When using MySQL, it’s important to keep backups of your databases to ensure you are able to restore them in the event of data loss. Downloading copies in the form of .sql files, can save you unnecessary stress and prevent future headaches. By using MySQL to import a SQL file, you can even create new databases based on your existing data.
Let’s get started by covering how to make a copy of your MySQL database.
Creating a MySQL Backup using the Command Line
Thanks to MySQL’s built-in command line utilities, making backups of your MySQL database is easy. By using the mysqldump command available with your MySQL installation (located in the bin directory), you can easily dump a MySQL Database to a SQL file by following these three simple steps:
- First, log in to your server using root user
- Now, use the following command to make a copy of your MySQL database using the mysqldump utility.
mysqldump –u[username] –p[password] [database_name] > [dump_file].sql
*Note: you will need to replace the names in the command above with those specific to you. Of course, “username” and “password” will need to be replaced with your MySQL username and password. You’ll also need to replace “database_name” with the name of the specific database you wish to copy and “dump_file” with the name you’d like to give the .sql file you are creating.

- Lastly, to make sure the command was executed and the backup file was created, on the same path use the command:
ls –l
You should see the database backup file listed now.
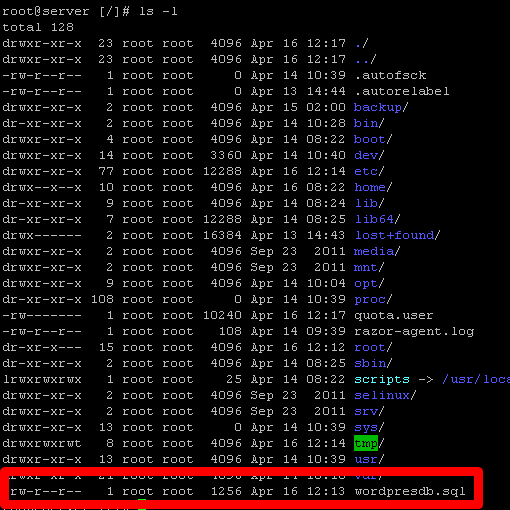
In addition to making a backup of an entire database, mysqldump can be used to make a copy of a specific table within a database as well. To copy a specific table, use the following command:
mysqldump –u[username] –p[password] [database] [table_name] > [dump_file].sql
*Note: same as above, you will need to replace “table_name” with the name of the specific table you are trying to copy.
Importing a MySQL Database Using a .sql File
After creating a backup of your MySQL database, the .sql file can be used to restore that database should anything happen to it. To restore your database simply use the command:
mysql –u[username] –p[password] [database_name] < [dump_file].sql
Additionally, the same .sql file can be used to create a new database as well. To import your .sql file into a new database, just use the following command:
mysql –u[username] –p[password] [new_database_name] < [dump_file].sql
After the process is complete, you should see two databases that are similar but have different names.
Popular Links
Looking for more information on MySQL? Search our Knowledge Base!
Interested in more articles about Databases? Navigate to our Categories page using the bar on the left or check out these popular articles:
- View the Contents of a Table in a SQL Server Database Using Enterprise Manager
- How to Install SQL Server Management Studio 2017 on Windows Server 2019
- How to Install SQL Server 2012 Express on Windows Server 2012
Popular tags within this category include: MySQL, MSSQL, phpMyAdmin, PostgreSQL, and more.
Don’t see what you’re looking for? Use the search bar at the top to search our entire Knowledge Base.
The Hivelocity Difference
Seeking a better Dedicated Server solution? In the market for Private Cloud or Colocation services? Check out Hivelocity’s extensive list of products for great deals and offers.
With best-in-class customer service, affordable pricing, a wide-range of fully-customizable options, and a network like no other, Hivelocity is the hosting solution you’ve been waiting for.
Unsure which of our services is best for your particular needs? Call or live chat with one of our sales agents today and see the difference Hivelocity can make for you.